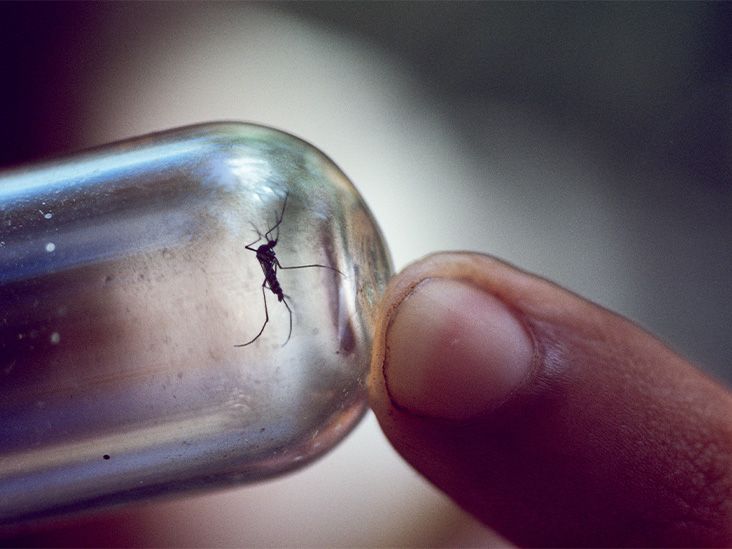
No, there is no research to support that mosquitoes can transmit sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, they can transmit mosquito-borne diseases, such as malaria, Zika, and Dengue fever.
Mosquitoes are small insects that can pass some diseases onto humans. Female mosquitoes possess a tube-like mouthpart known as a proboscis. They use this to pierce the skin of humans and animals to draw blood. They use the nutrients from the host blood to produce eggs.
While obtaining a blood meal from a host, the female mosquito injects its saliva into the skin. Its saliva prevents blood clots, allowing it to ingest blood. Mosquitoes do not naturally carry infections but can acquire them after drinking blood containing an infection. A mosquito can then act as a vector, or carrier, for a number of diseases and transmit them to humans.
By definition, a sexually transmitted infection (STI) is a microorganism, such as a virus, that
As mosquitoes do not inject people with blood, they can only pass on pathogens that can survive in their saliva.
Although it is possible for humans to pass STIs to another person through saliva, there is no research to support that mosquitoes can pass STIs to people through their saliva. This is likely because these pathogens do not have adaptations to replicate or survive in mosquitoes.
However, other pathogens do possess traits that enable them to survive and replicate in the saliva of mosquitoes. When a mosquito is carrying these viruses or pathogens, it can transmit them when biting a person.
Mosquito-borne diseases refer to any disease that a mosquito is able to transmit to a human. This happens when it feeds on a host with an infection and swallows any viruses or parasites present in the blood. It can then spread these pathogens to the next person it bites through its saliva.
Mosquitoes typically transmit viruses and parasites not common or present in the continental United States. When people travel overseas to areas with mosquitoes, such as tropical and subtropical areas, it’s important to try to avoid mosquito bites.
There are different species of mosquitos that can spread disease. These include:
- Aedes mosquitoes
- Anopheles mosquitoes
- Culex mosquitoes
Diseases mosquitos can transmit
Before traveling, it is advisable for people to research what diseases or health risks are a concern at their destination. They can verify the risk at their destination using this tool from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- DEET
- picaridin, also known as KBR 3023 or icaridin
- IR3535
- oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE)
- para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
People can also take other measures to avoid mosquito bites. These
Additionally, local governments and mosquito control programs can use
Mosquito-borne diseases refer to diseases a mosquito can transmit to people. Examples include malaria, Dengue fever, and Zika. Although mosquitoes can pass on certain diseases, this does not include STIs. STIs are unable to survive in a mosquito and, therefore, cannot be transmitted through mosquito bites.
To prevent mosquito-borne diseases, people should attempt to avoid mosquito bites. Effective methods include using EPA-registered insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and covering gaps in walls, doors, and windows.